 Contributed by Todd Perry, CEO, PPM Consultants, Inc
Contributed by Todd Perry, CEO, PPM Consultants, Inc
As we approach the mid-century mark, the landscape of energy consumption in the United States is poised for significant transformation. Petroleum, a cornerstone of modern industry and transportation, faces a complex future shaped by shifting economic priorities, technological innovation, and environmental imperatives. Predicting the trajectory of petroleum consumption requires examining current trends, evaluating potential scenarios, and considering the global and regional context.
The Current State of Petroleum Consumption
Petroleum remains the largest single energy source in the United States, powering transportation, industry, and residential heating. In 2022, the U.S. consumed approximately 20.3 million barrels of petroleum per day, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). Transportation accounted for nearly 70% of this demand, with personal vehicles and freight transportation leading the way.
However, changes are already underway. Advances in fuel efficiency, the rise of electric vehicles (EVs), and growing awareness of environmental concerns have begun to slightly alter consumption patterns. As these trends accelerate, they set the stage for significant shifts in how petroleum is used—and how much is needed—in the decades ahead.
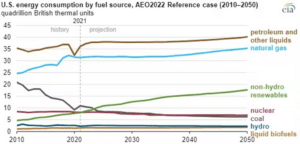
The following chart from the EIA’s Annual Energy Outlook 2022 highlights projected energy consumption by fuel source through 2050.
This chart shows that while petroleum and other liquids remain a significant part of the energy mix, the growth of renewables and gradual adoption of EVs and alternative fuels are reshaping the landscape.
Regional Spotlight: The Gulf South and Louisiana
The Gulf South, particularly Louisiana, has long been a hub of petroleum production and consumption. Louisiana’s economy is deeply tied to the oil and gas industry, making it one of the regions most resistant to moving away from petroleum-based energy. Gasoline consumption in Louisiana’s transportation sector has historically been among the highest in the nation, driven by:
- Geography: The state’s sprawling rural areas and low-density urban centers make personal vehicles the dominant mode of transportation.
- Cultural Factors: A long-standing reliance on traditional energy sources has created strong consumer and industrial preferences for petroleum.
- Economic Dependency: Louisiana’s significant oil refining and petrochemical industries mean local jobs and tax revenues are closely tied to petroleum.
Barriers to Transition in Louisiana
While the national conversation has focuses on renewable energy and electrification, Louisiana’s transition away from petroleum faces several challenges:
- Demographics and Infrastructure
Louisiana’s population includes a high percentage of rural and low-income households. These demographics are less likely to adopt costly alternatives like EVs due to:
- High upfront costs: EVs and associated charging infrastructure require significant initial investments.
- Limited charging network: Rural areas often lack the infrastructure needed to support EVs.
- Industrial Reliance
The petrochemical industry, a major economic driver in Louisiana, depends heavily on petroleum products. Transitioning to alternative fuels or electrification for industrial applications will require substantial technological advancements and capital investments.
- Slow Policy Evolution
Local and state policies in Louisiana have historically prioritized oil and gas development. Without aggressive incentives for renewable energy and EV adoption, which would be an ill-advised policy because the dollars would be much better invested in more impactful areas, the region is likely to lag behind national trends.
Projections Through 2050
Various projections offer a glimpse into the future of petroleum consumption in the U.S. The EIA’s Annual Energy Outlook 2023 presents multiple scenarios:
- Reference Case: Petroleum demand remains relatively stable, with modest declines due to increasing efficiency and gradual EV adoption.
- High Oil Price Scenario: High costs drive faster adoption of alternatives, leading to a sharper decline in petroleum use.
- Low Oil Price Scenario: Affordable petroleum discourages rapid EV uptake and renewable energy investment, maintaining higher levels of demand.
These scenarios indicate that Louisiana and the Gulf South’s petroleum consumption decline will be slower than in other regions due to entrenched industrial, economic, and cultural factors.
Key Drivers of Change
Several factors will shape the future of petroleum consumption in Louisiana and the broader U.S. by 2050:
Technological Advancements
The future of transportation remains uncertain as electric vehicle adoption experiences mixed trends. While EVs continue to gain attention as a cleaner alternative, adoption rates are currently facing challenges due to economic uncertainties, reduced subsidies, and high manufacturing costs. In Louisiana, adoption is expected to progress more slowly, influenced by limited charging infrastructure and the relatively high cost of EV ownership. As a result, technological advancements in hybrid vehicles and improved fuel efficiency for internal combustion engines may play a larger role in reducing petroleum dependence in the near term.
Policy and Regulation
Environmental policies, such as stricter fuel efficiency standards and emissions regulations, will influence petroleum demand. In Louisiana, policies that incentivize EV adoption and alternative fuels will face a slow, if any, adoption.
Consumer Behavior
Public sentiment around sustainability is growing, influencing purchasing decisions. However, in regions like Louisiana, where energy prices and availability significantly impact households, cost-effective alternatives to petroleum must be compelling to garner any real traction.
Potential Scenarios for 2050
The trajectory of petroleum consumption will depend on the interplay of economic, technological, and regulatory factors. Three potential scenarios highlight the range of possibilities:
- High Demand Scenario: Economic growth and low oil prices sustain high petroleum consumption, with demand concentrated in freight, aviation, and industrial applications.
- Rapid Transition Scenario: Aggressive EV adoption, renewable energy expansion, and strict regulations lead to a sharp decline in petroleum use, with alternative fuels dominating the energy mix.
- Balanced Transition Scenario: Moderate policy changes and steady technological advancements result in a gradual decline in petroleum consumption, with significant variation across sectors.
Charting the Path Forward
Managing the future of petroleum consumption in Louisiana and the U.S. requires a balanced approach. Policymakers must choose sensible investments in alternative energy while ensuring that industries reliant on petroleum have viable options to operate efficiently. Stakeholders in the energy sector must innovate to improve productivity and meet the evolving demands of consumers and industries.
As we look ahead to 2050, the Gulf South and Louisiana have an opportunity to lead in shaping a resilient energy future. The region can achieve a thoughtful transition that balances economic growth with environmental responsibility by leveraging technology, policy, and market dynamics.
For expert guidance in navigating environmental challenges in this shifting landscape, contact PPM Consultants today.

